50% of businesses are either intending to update their cloud-based ERP systems or are in the process of purchasing one (Technology Evaluation Centres, 2022). Cloud-based ERP systems have revolutionised how modern businesses manage everything from inventory to accounting. More than ever, companies of all sizes are thinking about cloud ERP.
To remain at the top of innovation, you must know cloud ERP and how it may benefit your company. Let’s get a thorough breakdown of cloud-based resource planning software.

Explaining cloud-based ERP software
1. Cloud-based ERP meaning: The glossary of terms
ERP stands for “enterprise resource planning’’ - typically a suite of integrated applications that businesses can use to manage data across the departments. “Resources” can be (but are not limited to) materials, employees, capital, equipment, and more.
Cloud-based ERP is software provided and managed in the cloud. This software typically goes through regular monthly maintenance and updates without costs or disruptions to it. Its scalability allows you to add more users or resources as needed.
You will encounter numerous concepts around cloud-based ERP. So here are important terms we have gathered for you before investing:
 Cloud-based ERP - The glossary of terms
Cloud-based ERP - The glossary of terms
2. Cloud-based ERP vs On-premise ERP
Every system has benefits and drawbacks, and right now we'll review to see which would be the best for your business:
2.1. Cost-efficiency
Because cloud ERP is offered "as a service," your subscription charge is determined by the ERP's functional scope. This can include user count, storage and compute resources. Budgeting is made simpler when expenses are adjusted to meet your requirements.
For on-premises ERP, there are significant up-front and ongoing costs in purchasing and maintaining the hardware (servers, server rooms, cooling systems, etc.) and software.
2.2. Data security
The cloud-based ERP stores your data on the vendor's cloud, which is accessed via a web application. This method aims to use a variety of encryption and access management protocols. Also, the vendor will provide regular security upgrades.
On-premise systems give you complete control over data. As a result, your team must be careful about data security policies and efficiency to avoid potential risks.
2.3. Customisation
Cloud ERP services are typically limited in terms of features. But they do allow for some customisation for an additional cost.
On-premise ERP allows you to customise extensively to meet your specific demands. After all, the assets are all there, and you can arrange them any way you see fit. However, this requires extra costs and may result in many operational setbacks like extended downtime.
2.4. Implementation
Cloud ERP deployment, on the other hand, takes less time and costs less upfront. However, customisation is restricted to the functionality provided by the vendor.
With on-premise ERP, your business is responsible for the implementation, and the process takes a long time. Depending on the type of ERP and features, a deployment may take up to 6 months. Also, there are significant upfront costs for hardware infrastructure and personnel. However, customisation is greater.
2.5. Scalability
Cloud ERP benefits from cloud auto-scaling features. This allows it to use as many resources as needed.
The hardware of on-premise ERP restricts its scalability. These limits require you to plan for expansion and expand the system properly.
2.6. Maintenance
With cloud ERP, the vendor manages the operation independently and updates the system's functionality and security architecture regularly. You only need to have a few maintenance personnel to oversee deployment and integration.
Using an on-premise solution, your business is responsible for everything. This element requires training or hiring specialised personnel for deployment and technical support.
3. The key components of cloud-based ERP systems
All cloud-based ERP software offers a range of versatile and adaptable functionalities. The types of modules that you choose to adopt are determined by your industry and specific requirements. Commonly, a modern cloud ERP module includes:
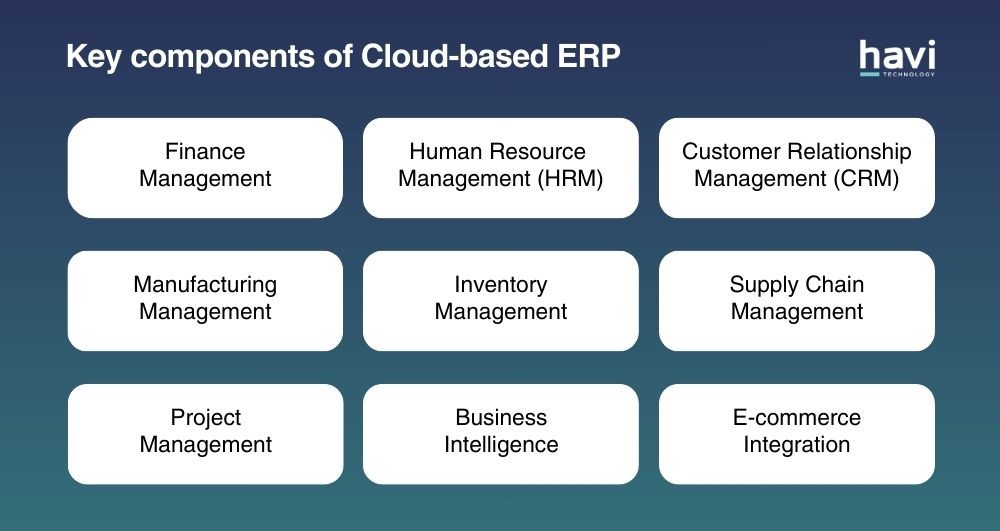
Key components of Cloud-based ERP
- Finance Management: Manages key financial activities such as accounts payable/receivable, budgeting, or asset management
- HRM: Manages employee data, payroll, recruitment, training, performance evaluation, etc
- CRM: Manages interactions with customers and tracks customer data through sales management, marketing automation, etc
- Manufacturing Management: Manages manufacturing tasks such as product planning, materials sourcing, production scheduling, quality control, etc
- Inventory Management: Manages inventory including raw materials, components, finished products, warehousing and processing
- Supply Chain Management: Manages the flow of goods and services, including inventory management, order management and logistics
- Project Management: Manages the planning, execution, and tracking of projects through scheduling, resource allocation, time tracking, etc
- Business Intelligence: Includes data analysis tools that help you make sense of data
- E-commerce Integration: Integrates e-commerce data, including online transactions, customer interactions, and inventory management.
4. The main types of cloud-based ERP software
It is crucial to know the different types of software and make the best choice for your company.
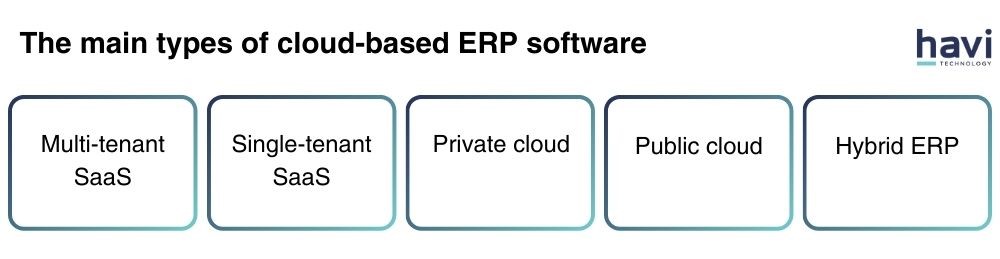 The main types of cloud-based ERP software
The main types of cloud-based ERP software
- Multi-tenant SaaS: Every customer shares the same single code base. The vendor handles all maintenance and upgrades. Others cannot access the database. Generally, these solutions are more cost-effective than other kinds of cloud ERP
- Single-tenant SaaS: Large companies often take advantage of this, and each uses its own database. The vendor handles all updates and maintenance. These solutions give you a great deal of control over your information and workflows
- Private cloud: The vendor manages the infrastructure and the business owns it. Although they cost more than public clouds, private clouds provide a higher level of protection. Businesses that handle sensitive data like healthcare providers, frequently use private clouds
- Public cloud: You use the internet to access the infrastructure - owned by the vendor. Although they are less costly than private clouds, public clouds pose security threats. It is important to make sure that your data is encrypted while it is in transit and while using a public cloud
- Hybrid ERP: A public and private cloud are combined to form a hybrid cloud. You can store less sensitive data on a public cloud and keep sensitive one on a private cloud when using a hybrid cloud. Accordingly, you can benefit from both public cloud cost reductions and maintain data security.
5. Calculating the main costs
Commonly, the ERP system you select will affect its total cost. Pricing is subjective and takes many factors into account. Looking at the ERP base cost and ROI will help you justify the investment cost. The most obvious costs include hardware (for private Cloud ERP), software licensing, per-user, initial implementation, data conversion, training and customisation.
However, keep in mind that ERP pricing structures vary by system when comparing costs. It is advisable to account for any unstated expenses. These could be:
- The amount of time your employees need to learn how to integrate the system and create procedures
- Future adjustments to the system in response to shifting requirements
- Updates for software
- More coaching and training as your company evolves.
The bottom line is that before selecting an ERP system, make sure you do your research on cost. Havi Technology - Odoo’s Gold Partner in Australia, can assist you with this process by conducting a robust ERP service.
Cloud-based ERP advantages & disadvantages
The ups and downs when using cloud ERP may differ based on the size of your company. The following aspects may apply to your specific case:
The hardships:
- You might not be able to take full advantage of cloud ERP in the same ways that others can if you run a business that is prohibited by compliance from hosting or storing client information in the cloud.
- Getting support from key stakeholders may take longer if you run a large business with a sizable IT team before you can use cloud ERP. It can also be necessary to train one or more people who can support you internally when you need to collaborate closely with your ERP vendor.
- If your company is larger and has been using traditional ERP software for a while, you might need extra help from your ERP vendor for the migration.
The best parts:
- The accessibility that cloud-based ERP offers is advantageous if your company works with vendors and partners globally.
- A cloud-based ERP system can assist in facilitating business growth for those who are prepared to take their company to the next level of profitability and growth. With an ERP that is cloud-based, you may quickly expand your business to satisfy client needs and seize new opportunities.
- Cloud ERP can give you enterprise-level solutions at a fraction of the cost if you run a smaller company and cannot afford the on-premises technology.
Time to switch to cloud-based ERP
Now is the perfect time to make your move with cloud-based ERP.
The world has gone through significant change in the last several years, and businesses must adapt to the changing digital economy. Thousands of businesses worldwide, and presumably many of your rivals, could use cloud ERP, a robust modern option.
Nhận xét
Đăng nhận xét